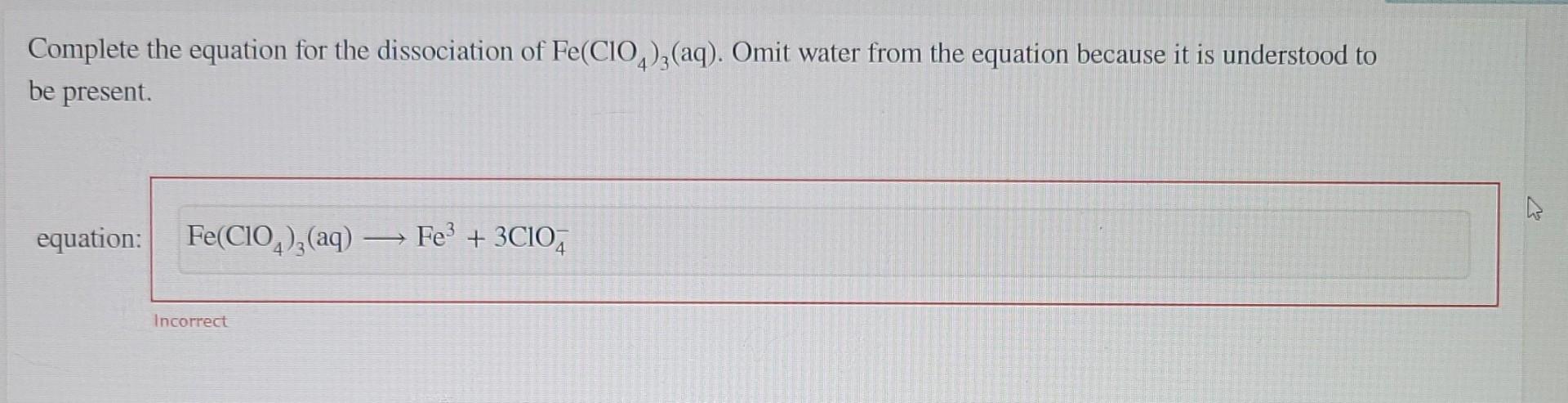
Complete this equation for the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq). Omit water from the equation because it is understood to be present.? This question marks the beginning of our journey into the fascinating world of chemical dissociation. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of this equation, exploring its components, influencing factors, and practical applications.
Brace yourself for a captivating exploration of the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq)!
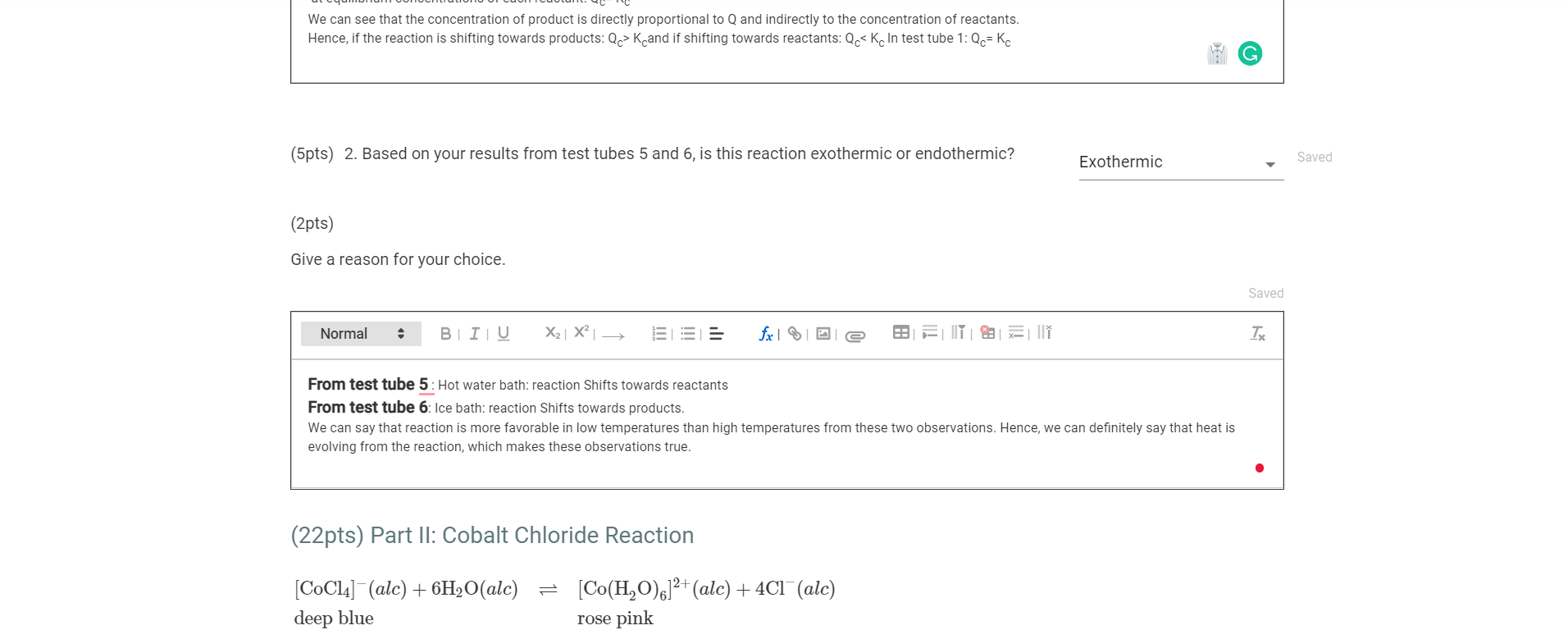
In this comprehensive guide, we will unravel the complexities of this equation, examining the ions formed during dissociation and the factors that govern the extent of dissociation. We will also venture into the practical realm, discovering how this dissociation finds applications in analytical chemistry, electrochemistry, and various industrial processes.
Prepare to be enlightened as we embark on this scientific adventure!
Dissociation Equation for Fe(ClO4)3(aq)
The dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq) occurs when it dissolves in water, separating into its constituent ions.
Balanced Dissociation Equation
The balanced dissociation equation for Fe(ClO4)3(aq), omitting water, is as follows:
Fe(ClO4)3(aq) → Fe3+(aq) + 3ClO4-(aq)
In this equation, Fe(ClO4)3 dissociates into Fe3+ and ClO4- ions.
Ions Formed
During dissociation, Fe(ClO4)3 breaks down into the following ions:
- Fe3+: Iron(III) cation
- ClO4-: Perchlorate anion
Factors Influencing Dissociation
The dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq) is influenced by several factors, including temperature, concentration, and solvent polarity. Understanding these factors is crucial for controlling and predicting the extent of dissociation in various chemical systems.
Temperature
Temperature plays a significant role in the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq). According to Le Chatelier’s principle, increasing the temperature of the solution favors the endothermic dissociation reaction, leading to a higher degree of dissociation. Conversely, decreasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium towards the association reaction, resulting in a lower degree of dissociation.
Concentration
The initial concentration of Fe(ClO4)3(aq) also affects its dissociation. Le Chatelier’s principle states that increasing the concentration of the reactants (Fe(ClO4)3(aq)) shifts the equilibrium towards the products (Fe3+(aq) and ClO4-(aq)), resulting in a higher degree of dissociation. Conversely, decreasing the initial concentration shifts the equilibrium towards the reactants, leading to a lower degree of dissociation.
Solvent Polarity, Complete this equation for the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq). Omit water from the equation because it is understood to be present.?
The polarity of the solvent used can significantly influence the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq). Polar solvents, such as water, favor the dissociation of ionic compounds by solvating the ions and reducing their electrostatic interactions. In contrast, nonpolar solvents, such as hexane, have a lower solvating ability and hinder the dissociation process, leading to a lower degree of dissociation.
Applications of Dissociation: Complete This Equation For The Dissociation Of Fe(ClO4)3(aq). Omit Water From The Equation Because It Is Understood To Be Present.?
The dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq) finds practical applications in various fields, including analytical chemistry, electrochemistry, and industrial processes.
Now that you know the equation for the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq), you might be wondering if you can get your car inspected in any county in Texas. The answer is yes, you can get your car inspected in any county in Texas, regardless of where you live.
Can A Car Be Inspected In Any County In Texas? This is because the Texas Department of Public Safety (DPS) has a network of inspection stations located throughout the state. So, no matter where you live in Texas, you can find a DPS inspection station near you.
Analytical Chemistry
In analytical chemistry, the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq) is utilized in:
- Spectrophotometry:The colored solutions formed due to the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq) can be analyzed using spectrophotometry to determine the concentration of iron ions in a sample.
- Titration:Fe(ClO4)3(aq) can be used as a titrant in redox titrations to determine the concentration of reducing agents.
Electrochemistry
In electrochemistry, the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq) is employed in:
- Electroplating:The iron ions released upon dissociation can be electroplated onto a cathode, forming a thin layer of iron.
- Batteries:Fe(ClO4)3(aq) can be used as an electrolyte in iron-air batteries, which are used in electric vehicles and other applications.
Industrial Processes
In industrial processes, the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq) is involved in:
- Water treatment:Fe(ClO4)3(aq) is used as a coagulant in water treatment plants to remove impurities and clarify water.
- Textile dyeing:Fe(ClO4)3(aq) is used as a mordant in textile dyeing to enhance the colorfastness of dyes.
- Leather tanning:Fe(ClO4)3(aq) is used in the tanning process of leather to improve its durability and resistance to water damage.
Final Wrap-Up
As we conclude our exploration of the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq), we hope you have gained a deeper understanding of this intriguing chemical phenomenon. The dissociation equation, influenced by factors such as temperature and concentration, provides valuable insights into the behavior of ions in solution.
Moreover, its applications in diverse fields highlight the practical significance of this dissociation. We encourage you to continue your quest for knowledge, delving further into the fascinating world of chemistry.
FAQ Summary
What is the balanced equation for the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq)?
Fe(ClO4)3(aq) → Fe3+(aq) + 3ClO4-(aq)
How does temperature affect the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq)?
Increasing temperature generally increases the extent of dissociation.
What is the role of Le Chatelier’s principle in understanding the dissociation of Fe(ClO4)3(aq)?
Le Chatelier’s principle helps predict how the dissociation equilibrium will shift in response to changes in temperature, concentration, or the addition of common ions.